D.Network Core Concepts
Components Diagram
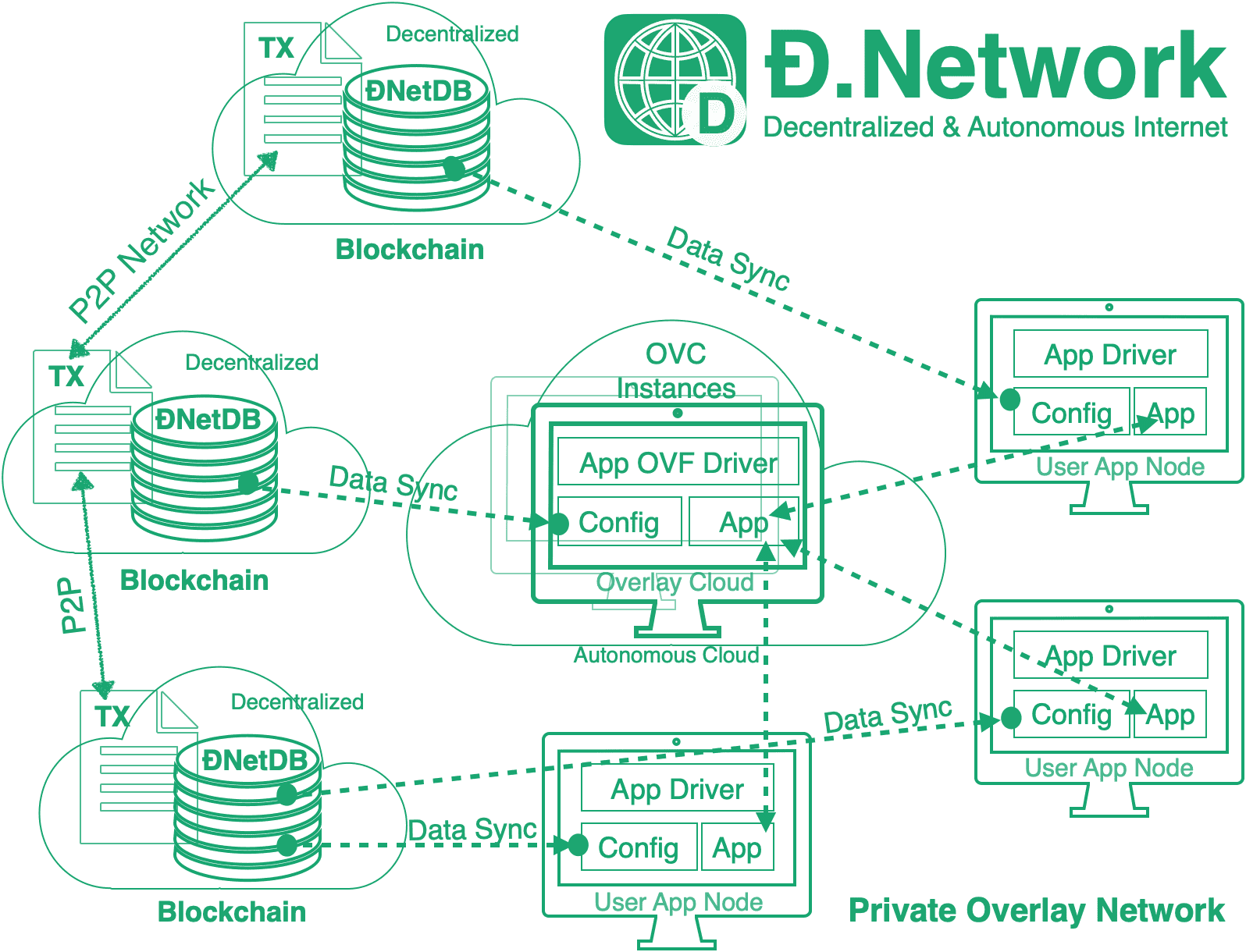
Private Overlay Network
The private overlay network is referred as
dnetorĐNetorDNet.
ĐNet is an abstract private overlay network, attached to the Internet underlayer as end points. The main attributes of the ĐNet are:
- A list of member nodes as identified by their public key
- Directive or pointer to the associated Overlay Cloud (OVC).
The OVC instantiates the abstract ĐNet with the protocols, capabilities and features which are specific for each ĐNet.
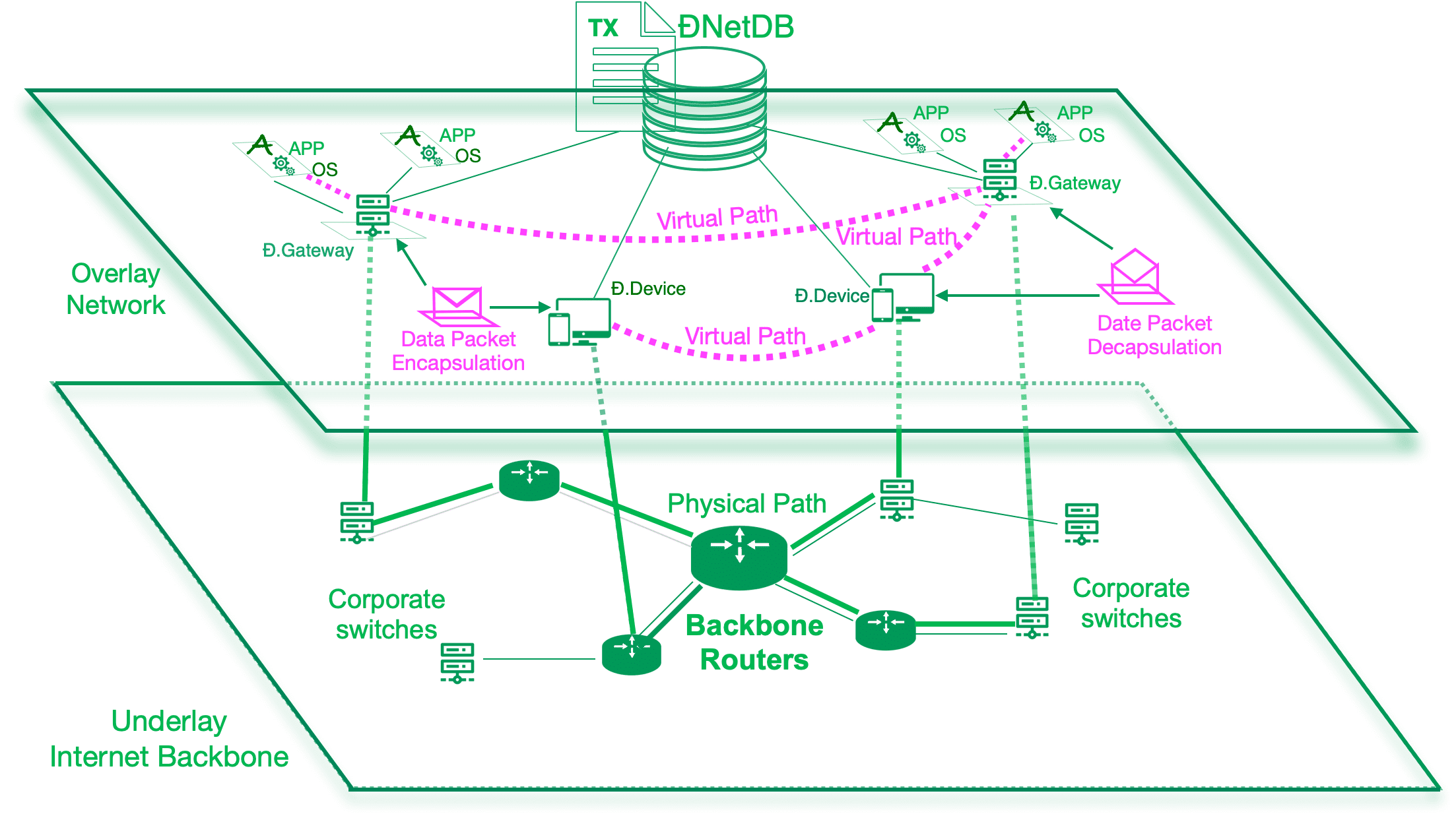
ĐNet DB
ĐNetDB is the meta-data for the DNet. A record in the ĐNetDB defines a ĐNet, e.g. adding a new record means creating a new ĐNet. The database CRUD operation logs are stored on blockchain,similar to Bitcoin's transaction ledger. Each dnet record stores a list of nodes and directive or pointer to the associated OVC. Similar to Bitcoin's token, the dnet record belongs to its creator and is locked by creator's public key. Only its creator can use signature script to unlock it and add/delete nodes & assign OVC.
Each dnet has a pair of crypto keys and the hash of the public key serves as the dnetid. All member nodes will receive the dnet private key out-of-band. The private key can be used to decrypt dnet's records.
ĐNet Node
The nodes are the networking elements to get connected and run App within a ĐNet. It can be any device, like computer, mobile phone or embedded device. A node lives within the scope of individual ĐNet and it can be in multiple ĐNets at the same time. DNet Node is the host to run DNet App.
The two main attributes of node are for networking:
- The crypto keys, including both private key & public key (PubKey), Its PubKey serves as its Crypto ID in the address namespace, similar to the Bitcoin's wallet address. The PubKey is also used to encrypt traffic.
- Assigned virtual IPv4/IPv6 address. The virtual IP addess is the bridge to the Layer 3 network and used to set the routing table.
The node does NOT need a public IP address, it will instead use OVC to find peer nodes.
Overlay Cloud
Overlay Cloud (OVC) is the cloud backend for each ĐNet. The OVC defines the protocols, capabilities and features for each ĐNet. OVC is the concrete implementation of the abstract ĐNet as defined in blockchain. For example, an OVC with SD-WAN control and data plane capability creates a Layer 3 overlay network for the ĐNet member nodes. An Instant Message (IM) server as the OVC enables the ĐNet member nodes to chat with each other. Since the OVC has no access to the encrypted traffic, the OVC can be either self-managed or outsourced without sacrificing privacy.
The two main attributes of overlay cloud are for cloud backend:
- The crypto keys, including both private key & public key (PubKey), Its PubKey serves as its Crypto ID in the address namespace, similar to the Bitcoin's wallet address. The PubKey is also used to encrypt traffic.
- The public IPv4/IPv6 address for the dnet member nodes to connect to.
The above meta data can be encrypted with dnet public key and only the dnet member nodes can decrypt.
Since one of OVC major roles is the rendezvous point for all member nodes, it usually has public IP address. The OVC can compose a cluster of nodes for high availability. For third-party OVC, the dnet owners usually subscribe the OVC services. The subscription payment is enabled with ĐNet token smart contract.
Learn more about Overlay Cloud
ĐNet App
ĐNet App is the software running on ĐNet Node. The interface to ĐNetDB is generic and new App and OVC can be easily added using the ĐNet SDK.
The first implemented ĐNet App is a Layer 3 Overley Network, also known as SD-WAN. The OVC cloud backend is the control plane and data plane for the SD-WAN.
The benefit of the decentralized SD-WAN is that the core meta info are securely stored in blockchain and the cloud backend can be outsourced without sacrificing privacy. The maintenance of cloud backend is reduced to minimal if self-managed.
Crypto ID is paramount
Like IP address is fundamental for Internet, Crypto ID is paramount on ĐNet platform. The namespace on ĐNet is the Crypto ID for both ĐNet and its member node. A ĐNetID is associated with a list of NodeIDs to form a private overlay network.
The assigned Virtual IP for each node serve as the bridge from Crypto ID to the Layer 3 IP network and standard TCP/IP applications.
| Crypto ID | Description | Public Key |
|---|---|---|
| dnetID | dnet record ID | hash of dnet pubkey |
| nodeID | node crypto address | hash of node pubkey |
| ovcID | ovc record ID | hash of ovc pubkey |
ID and Location Split
Internet uses IP addresses and relies on the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) for allocating IP address and IP routing, and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to exchange routing information between Autonomous Systems (AS) Zones. The location information or the address-book is implicitly carried in the subnet mask or the hierarchical structure of each TCP/UDP packet. In many use cases, it is desired to split the ID and location for flexibile networking.
Software Defined WAN
A Software-defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) is a virtual WAN architecture that allows enterprises to leverage any combination of transport services to securely connect users to distributed applications. An SD-WAN uses a centralized control function to securely and intelligently direct traffic across the WAN. This increases application performance and delivers a high quality user experience, resulting in increased business productivity, agility and reduced costs for IT.
DNetwork is a decentralized platform to create SD-WAN easily and secure.
